Variable Cost: Definition, Formula, and Examples
- Posted by admin rcs
- On January 9, 2024
- 0
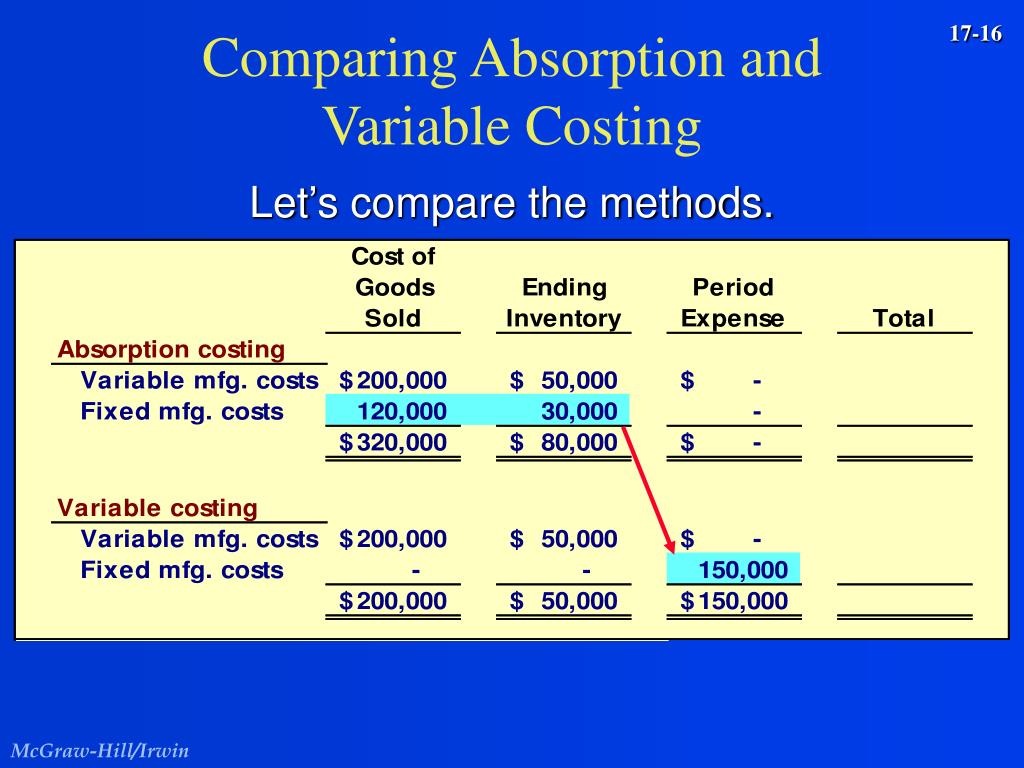
So, you’re taking variable cost per unit into account, you’re making $10 per mug. Actively seeking ways to reduce variable costs and continuously adjusting strategies can have a positive impact on both profitability and the overall success of a business. To better explain this concept and differentiate variable and fixed costs, we’ll use a few examples to help you understand how they may apply to your industry. These costs have a mix of costs tied to each unit of production and a fixed cost which will be incurred regardless of production volume.
Packaging and Shipping Costs
Managers can control variable costs more easily in the short-run by adjusting output. It’s important to differentiate variable costs from fixed costs, as they have different impacts on a business’s financial health and decision-making processes. Fixed costs are expenses that remain constant, regardless of changes in production or sales volume.

Calculating Variable Costs
Both costing methods can be used by management to make manufacturing decisions. Both can also be used for internal accounting purposes to value work in progress and finished inventory. Variable costing isn’t allowed for external reporting because it doesn’t follow the GAAP matching principle. It fails to recognize certain inventory costs in the same period in which revenue is generated by the expenses. Mastering the analysis of how costs behave enables companies to make astute decisions around budgeting, pricing, production levels, and elevating efficiency, thereby driving business sustainability and growth.
What are the primary components that make up variable costs?
- In this guide, we’ll break down everything you need to know about variable costs.
- By embracing lean techniques, businesses can effectively reduce their variable costs and improve overall efficiency.
- One of those cost profiles is a variable cost that only increases if the quantity of output also increases.
- Variable costing is a concept used in managerial and cost accounting in which the fixed manufacturing overhead is excluded from the product-cost of production.
When the manufacturing line turns on equipment and ramps up production, it begins to consume energy. When it’s time to wrap up production and shut everything down, utilities are often no longer consumed. As a company strives to produce more output, it is likely this additional effort will require additional power or energy, resulting in increased variable utility costs. These employees will receive the same amount of compensation regardless of the number of units produced. For others who are tied to an hourly job, putting in more direct labor hours results in a higher paycheck.
Understanding Variable Costs
For example, if no units are produced, there will be no direct labor cost. Some labor costs, however, will still be required even if no units are produced. Certain positions may be salaried whether output is 100,000 units or 0 units, such as an accountant or lawyer of the firm. building a dcf using the unlevered free cash flow formula fcff is a valuable management tool but it isn’t GAAP-compliant and it can’t be used for external reporting by public companies. A company may also have to use absorption costing which is GAAP-compliant if it uses variable costing.
Variable costs vs fixed costs
Most companies will use the absorption costing method if they have COGS and it may be required for external reporting purposes because it’s the only method that complies with GAAP. Companies may decide that absorption costing alone is more efficient to use. Once you’ve done everything you can to tighten up variable costs for your business, there are other ways to lower the cost of doing business. If you’re having trouble seeing how these techniques could apply to your business, consider hiring a business operations or managerial accounting consultant with experience in your industry. They may be able to find loopholes, shortcuts, and tricks of the trade that can help you reduce your variable costs. Watch this short video to quickly understand the main concepts covered in this guide, including what variable costs are, the common types of variable costs, the formula, and break-even analysis.
The firm offers bookkeeping and accounting services for business and personal needs, as well as ERP consulting and audit assistance. Variable costs can guide businesses in determining how to allocate resources optimally. PQR is a chocolate factory and has the costs, sales, and production information as per the below template. Variable costs are usually viewed as short-term costs as they can be adjusted quickly. For example, if a company is having cash flow issues, it may immediately decide to alter production to not incur these costs.
Variable costing is a cost accounting method for calculating production expenses where only variable costs are included in the product cost. The formula of variable costing only considers the direct cost and other variable manufacturing expenses incurred on each product unit. Variable costs are directly related to the cost of production of goods or services, while fixed costs do not vary with the level of production. Variable costs are commonly designated as COGS, whereas fixed costs are not usually included in COGS.
Wood is considered a variable cost because the price of it can change over time. By understanding variable costs, businesses can conduct cost-volume-profit analysis, optimize pricing strategies, and allocate resources efficiently. In general, companies with a high proportion of variable costs relative to fixed costs are considered to be less volatile, as their profits are more dependent on the success of their sales.
It can change its entire labor force, managerial as well as line workers. In summary, advanced concepts in variable costing, such as semi-variable costs and operating leverage, play a significant role in managerial decision-making. Companies that identify and analyze these aspects can better develop effective cost management strategies while maintaining financial stability in both high and low sales periods. By understanding how variable costs impact various industries, businesses can effectively manage expenses and implement strategies to reduce costs, thereby increasing profitability. If Amy were to shut down the business, Amy must still pay monthly fixed costs of $1,700. If Amy were to continue operating despite losing money, she would only lose $1,000 per month ($3,000 in revenue – $4,000 in total costs).



0 comments on Variable Cost: Definition, Formula, and Examples